Hybrid Orbital Theory : Overcoming the Limits of Atomic Orbitals
Early atomic orbital models could not explain real molecular shapes. For example, methane should show 90° bond angles, but experiments reveal 109.5°. Hybrid orbital theory solved this by combining s and p orbitals, explaining bond angles, directionality, and molecular geometry more accurately.
Simply add : S orbital + P orbital
Let me explain hybrid orbital through Methane, ethylene, and acetylene.
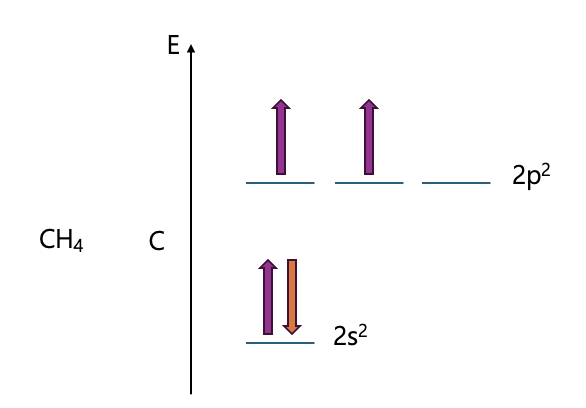
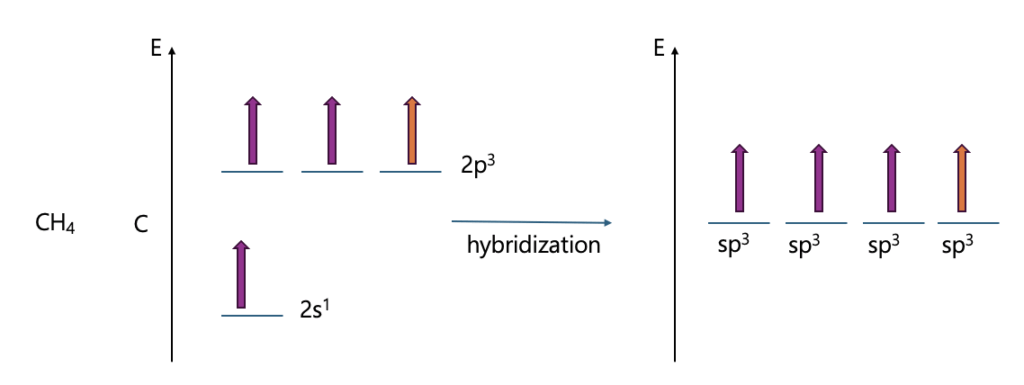
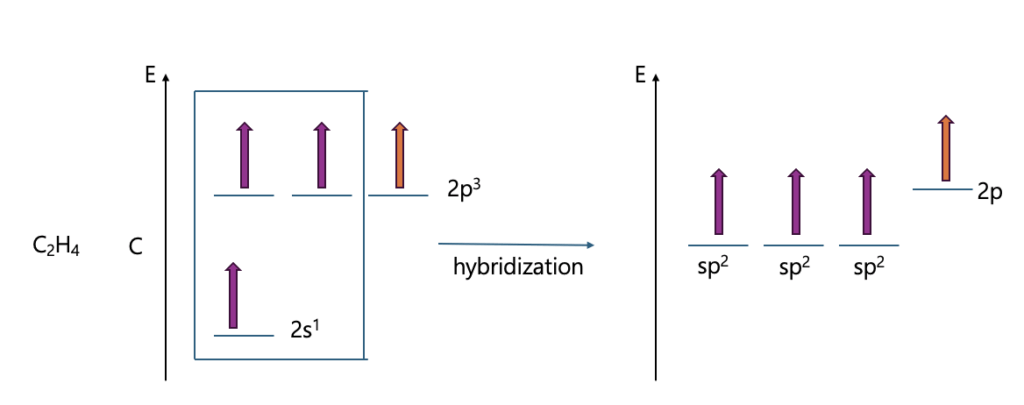
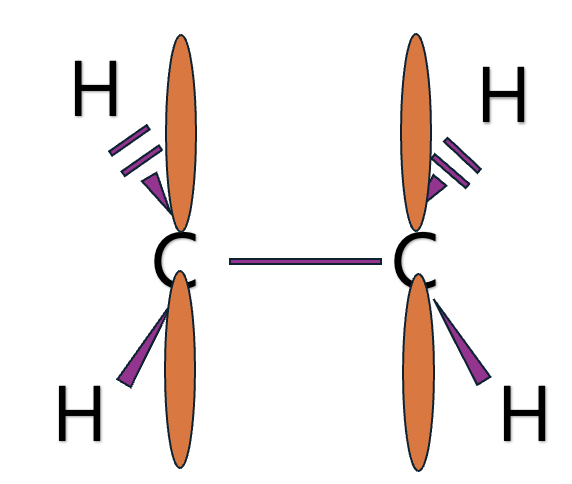
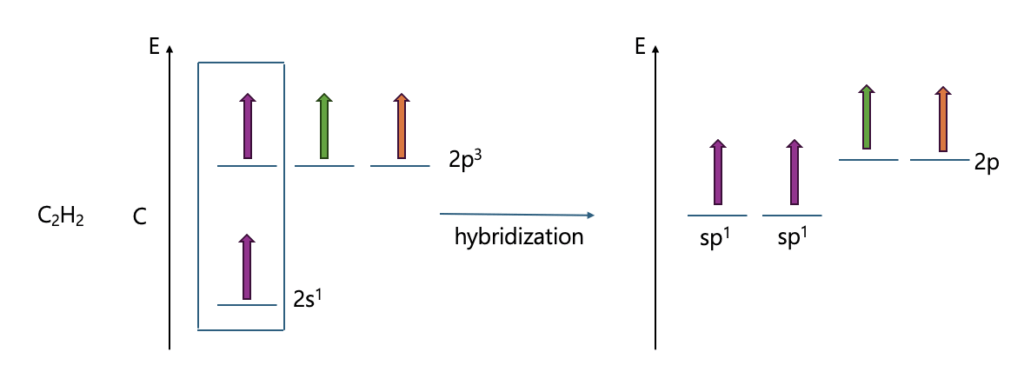
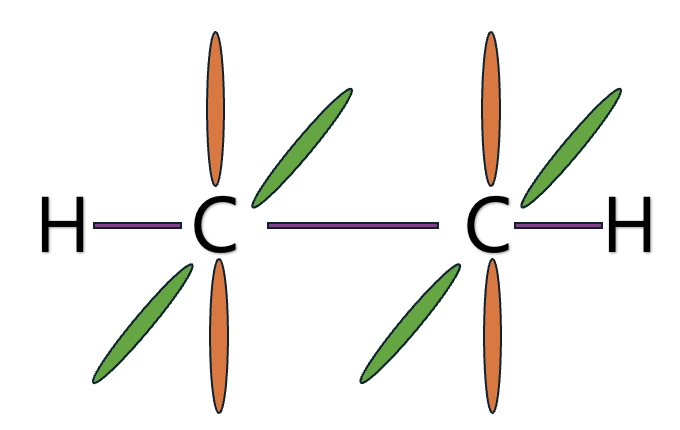
What if the S character gets bigger?
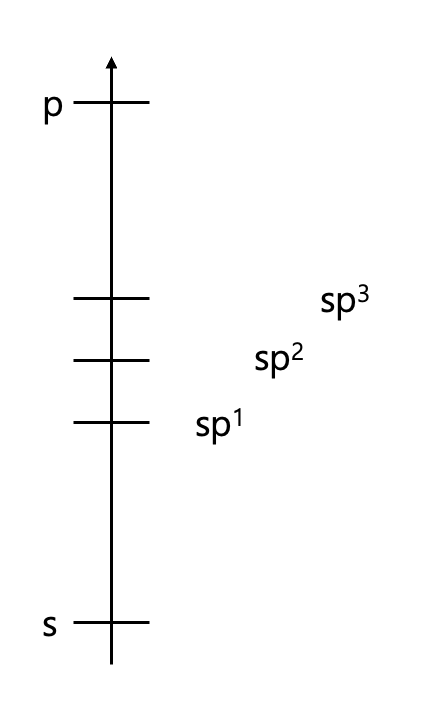
- Electronegativity ↑
- Bond length ↓
- Stability of anion ↑
